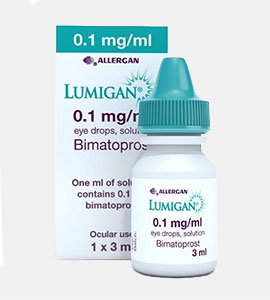
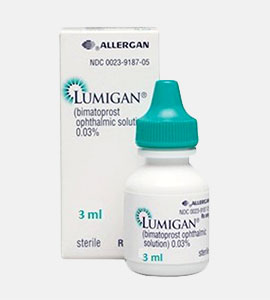
Latisse Generic (Bimatoprost)
* For illustration purpose only
Latisse Generic (Bimatoprost)
Short description
added to cart
-
Shippingavrg. 5-9 daysGuaranteed delivery time 16 daysGuaranteed delivery time 16 daysDosages mentioned (EU), are shipped inside Europe and guarantee faster time in delivery.
-
Payment






-
Upgrade and save. Add worth of items to cart and get free shipping
200 €




Latisse Generic (Bimatoprost)
Latisse (Bimatoprost) and Bimatoprost Ophthalmic Information
Latisse (Bimatoprost) Overview
Latisse, an anthropogenic form of the natural substance prostaglandin, is used to treat hypotrichosis, which is an abnormal growth of eyelashes. Bimatoprost, the active ingredient in Latisse, helps increase the growth, length, thickness, and darkness of eyelashes. Latisse may also be used for other purposes not listed in this manual.
Important Safety Information
Severe Reactions: Stop using Latisse and consult a doctor immediately if you experience severe eye irritation, eye pain, or changes in vision.
Allergies: Do not use Latisse if you are allergic to bimatoprost. Inform your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, allergies, and medications.
Pregnancy and Children: It is not known if Latisse will harm an unborn child. Notify your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breastfeeding. Do not give Latisse to a child without medical advice.
Using Latisse
Application: Apply Latisse every night. Follow all directions on the label. Do not use more than the recommended quantity, as it will not enhance effectiveness.
Timing: Use Latisse in the evening, unless instructed otherwise by your doctor. Avoid using it while wearing contact lenses. If you wear contacts, wait at least 15 minutes after applying Latisse before inserting them.
Bimatoprost Ophthalmic Use
Bimatoprost ophthalmic, commonly used for treating certain types of glaucoma and other causes of elevated intraocular pressure, works by increasing the outflow of fluid from the eye, thus reducing eye pressure. This medication may also be used for purposes not mentioned in this guide.
Important Safety Information for Bimatoprost Ophthalmic
Allergies: Do not use bimatoprost ophthalmic if you are allergic to bimatoprost.
Eye Conditions: Inform your doctor if you have a history of glaucoma, increased eye pressure, uveitis, or any swelling or infection around the eyes. Mention any past eye injuries or surgeries.
Color Changes: Bimatoprost may cause gradual changes in the color of your eyes, eyelids, or eyelashes, often resulting in increased brown pigmentation.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: It is not known whether bimatoprost will harm an unborn child or pass into breast milk. Consult your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breastfeeding.
Age Restrictions: Bimatoprost ophthalmic is not approved for use in individuals younger than 16 years of age.
Using Bimatoprost Ophthalmic
Dosage: The usual dose is one drop in the affected eye(s) each evening. Follow all instructions on your prescription label.
Contact Lenses: Do not use this medication while wearing contact lenses. Wait at least 15 minutes after applying bimatoprost before inserting contact lenses.
Application: Wash your hands before applying the drops. Avoid touching the dropper tip to your eye or other surfaces. Do not use if the liquid has changed color or contains particles.
Eye Injuries: Notify your doctor immediately if you experience any eye injuries, infections, or plan to undergo eye surgery.
Missed Dose
Latisse: If you miss a dose, apply it as soon as you remember. If it’s almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and continue with your regular schedule.
Bimatoprost Ophthalmic: Skip the missed dose and use the medication at the next scheduled time. Do not double up on doses.
Overdose
Latisse: An overdose of Latisse is not expected to be harmful.
Bimatoprost Ophthalmic: Overdose is unlikely to cause severe issues.
Avoid
Excessive Use: Avoid using more of either medication than directed, as it may reduce effectiveness or cause unwanted effects.
Other Eye Medications: Do not use other eye medications unless your doctor instructs otherwise.