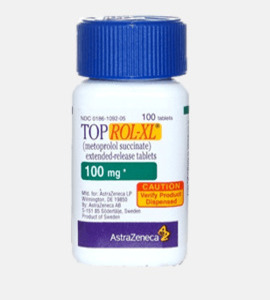
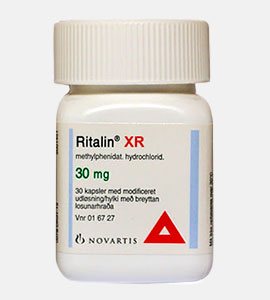
Ritalin (Methylphenidate) by Novartis
* Solo para fines ilustrativos
Ritalin (Methylphenidate) by Novartis
Descripción breve
Simplemente deja tu contacto a continuación




Ritalin (Methylphenidate) by Novartis
Therapeutic indications
Ritalin is indicated as a part of a comprehensive treatment programme for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children aged 6 years of age and over when remedial measures alone prove insufficient. Treatment must be under the supervision of a specialist in childhood behavioural disorders. Diagnosis should be made according to DSM criteria or the guidelines in ICD and should be based on a complete history and evaluation of the patient. Diagnosis cannot be made solely on the presence of one or more symptom.
The specific aetiology of this syndrome is unknown, and there is no single diagnostic test. Adequate diagnosis requires the use of medical and specialised psychological, educational and social resources.
A comprehensive treatment programme typically includes psychological, educational and social measures as well as pharmacotherapy and is aimed at stabilising children with a behavioural syndrome characterised by symptoms which may include chronic history of short attention span, distractibility, emotional lability, impulsivity, moderate to severe hyperactivity, minor neurological signs and abnormal EEG. Learning may or may not be impaired.
Methylphenidate treatment is not indicated in all children with this syndrome and the decision to use the drug must be based on a very thorough assessment of the severity and the chronicity of the child's symptoms in relation to the child's age.
Appropriate educational placement is essential, and psychosocial intervention is generally necessary. Where remedial measures alone prove insufficient, the decision to prescribe a stimulant must be based on rigorous assessment of the severity of the child's symptoms. The use of methylphenidate should always be used in the way according to the licensed indication and according to the prescribing/diagnostics guidelines.
Dose titration
Careful dose titration is necessary at the start of treatment with methylphenidate. Dose titration should be started at the lowest possible dose.
The maximum daily dose is 60mg.
Other strengths of this medicinal product and other methylphenidate containing products may be available.
Children: (over 6 years). Begin with 5mg once or twice daily (e.g. at breakfast and lunch), increasing the dose and frequency of administration if necessary by weekly increments of 5-10mg in the daily dose. Doses above 60mg daily are not recommended. The total daily dose should be administered in divided doses. Ritalin is not indicated in children less than 6 years of age.
If the effect of the drug wears off too early in the evening, disturbed behaviour and/or inability to go to sleep may recur. A small evening dose may help to solve this problem.
Long term (more than 12 months) use in children and adolescents
The safety and efficacy of long term use of methylphenidate has not been systematically evaluated in controlled trials. Methylphenidate treatment should not and need not, be indefinite. Methylphenidate treatment is usually discontinued during or after puberty. The physician who elects to use methylphenidate for extended periods (over 12 months) in children and adolescents with ADHD should periodically re-evaluate the long term usefulness of the drug for the individual patient with trial periods off medication to assess the patient's functioning without pharmacotherapy. It is recommended that methylphenidate is de-challenged at least once yearly to assess the child's condition (preferable during school holidays). Improvement may be sustained when the drug is either temporarily or permanently discontinued.
Dose reduction and discontinuation
Treatment must be stopped if the symptoms do not improve after appropriate dosage adjustment over a one-month period. If paradoxical aggravation of symptoms or other serious adverse events occur, the dosage should be reduced or discontinued.
• Adults
Ritalin Tablets are not licensed for use in adults with ADHD. Safety and efficacy have not yet been established in this age group.
• Elderly
Methylphenidate should not be used in the elderly. Safety and efficacy has not been established in this age group.
• Children under 6 years of age
Methylphenidate should not be used in children under the age of 6 years. Safety and efficacy in this age group has not been established.
• Hepatic impairment
Ritalin has not been studied in patients with hepatic impairment. Caution should be exercised in these patients.
• Renal impairment
Ritalin has not been studied in patients with renal impairment. Caution should be exercised in these patients.
Contraindications
• Known sensitivity to methylphenidate or to any of the excipients in Ritalin.
• Glaucoma
• Phaechromocytoma
• During treatment with monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors, or within a minimum of 14 days of discontinuing those drugs, due to risk of hypertensive crisis
• Hyperthyroidism or thyrotoxicosis
• Diagnosis or history of severe depression, anorexia nervosa/anorexic disorders, suicidal tendencies, psychotic symptoms, severe mood disorders, mania, schizophrenia, psychopathic/borderline personality disorder.
• Diagnosis or history of severe and episodic (Type 1) Bipolar (affective) disorder (that is not well controlled)
• Pre-existing cardiovascular disorders including severe hypertension, heart failure, arterial occlusive disease, angina, haemodynamically significant congenital heart disease, cardiomyopathies, myocardial infarction, potentially life-threatening arrhythmias and channelopathies (disorders caused by the dysfunction of ion channels)
• Pre-existing cerebrovascular disorders cerebral aneurysm, vascular abnormalities including vasculitis or stroke or known risk factors for cerebrovascular disorders
Special warnings and precautions for use
Methylphenidate treatment is not indicated in all children with ADHD and the decision to use the drug must be based on a very thorough assessment of the severity and chronicity of the child's symptoms in relation to the child's age.